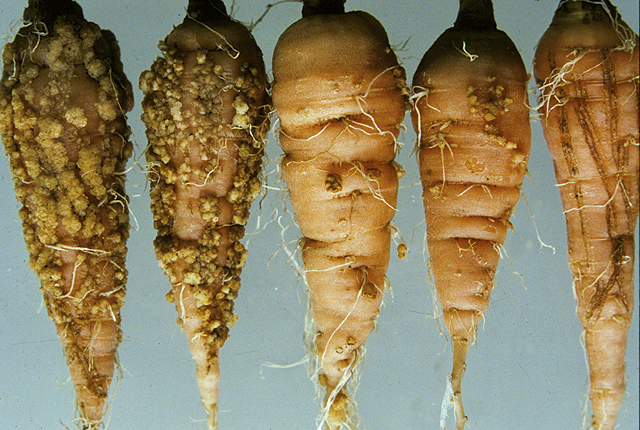
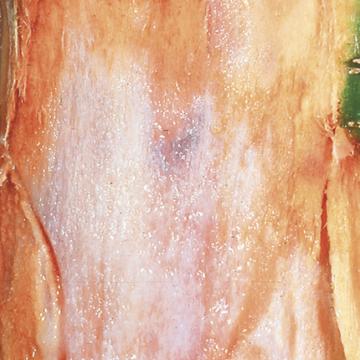DISEASE: Bacterial gall
HOST: Carrot
Root with many galls of different sizes.

Bacterial gall | Carrot
DISEASE: Bacterial gall
HOST: Carrot (Daucus carota)
PATHOGEN: Rhizobacter dauci
SOURCE: H. Kuwata
DISEASE: Bacterial gall
HOST: Carrot
Galls caused from inoculation of injured roots (left two) and uninjured roots (center two). Uninjured, noninoculated root (right).

Bacterial gall | Carrot
DISEASE: Bacterial gall
HOST: Carrot (Daucus carota)
PATHOGEN: Rhizobacter dauci
SOURCE: M. Goto
DISEASE: Bacterial gall
HOST: Cherry
Small gall on twig.

Bacterial gall | Cherry
DISEASE: Bacterial gall
HOST: Cherry (Prunus avium)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas syringae pv. cerasicola
SOURCE: H. Kamiunten, M. Goto
DISEASE: Bacterial gall
HOST: Wisteria (Japanese wisteria)
Multiple galls on trunk.

Bacterial gall | Wisteria (Japanese wisteria)
DISEASE: Bacterial gall
HOST: Wisteria (Japanese wisteria) (Wisteria floribunda)
PATHOGEN: Pantoea agglomerans pv. millettiae
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Erwinia herbicola pv. millettiae
SOURCE: M. Goto
DISEASE: Bacterial gall
HOST: Wisteria (Japanese wisteria)
Gall on branch.

Bacterial gall | Wisteria (Japanese wisteria)
DISEASE: Bacterial gall
HOST: Wisteria (Japanese wisteria) (Wisteria floribunda)
PATHOGEN: Pantoea agglomerans pv. millettiae
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Erwinia herbicola pv. millettiae
SOURCE: M. Goto
DISEASE: Carrot yellows
HOST: Carrot
Flowers with shoot proliferation (witches’-broom) (left). Healthy flower (right). Virescence and phyllody of flower parts are common.
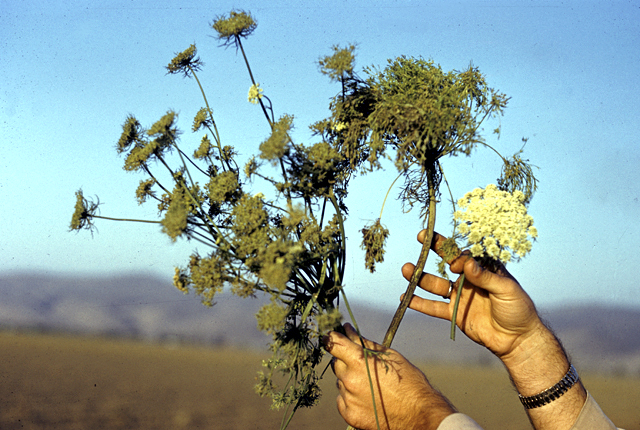

Carrot yellows | Carrot
DISEASE: Carrot yellows
HOST: Carrot (Daucus carota)
PATHOGEN: 'Candidatus Phytoplasma asteris'
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Phytoplasma Aster yellows group
SOURCE: M. Schroth
DISEASE: Carrot yellows
HOST: Carrot
Carrot with proliferation of roots. Initial symptoms include yellowing and narrowing of veins of young leaves. The entire leaf later becomes necrotic.

Carrot yellows | Carrot
DISEASE: Carrot yellows
HOST: Carrot (Daucus carota)
PATHOGEN: 'Candidatus Phytoplasma asteris'
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Phytoplasma Aster yellows group
SOURCE: G. S. Abawi
DISEASE: Foamy canker
HOST: Almond
White, macerated tissues near cambium region is characteristic of disease. Foam is usually associated with cankers. The disease is suspected to be bacterial but the causal agent has not been identified.
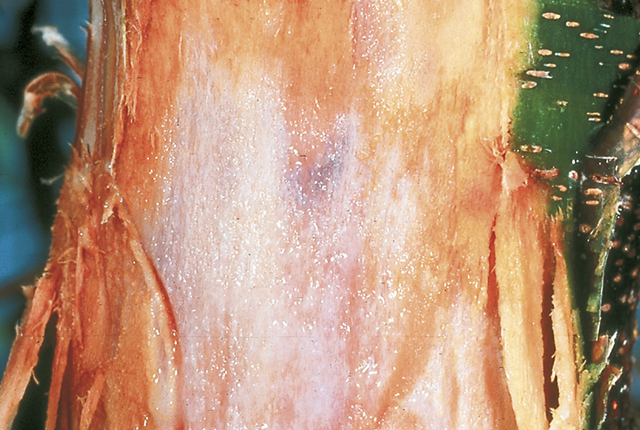
Foamy canker | Almond
DISEASE: Foamy canker
HOST: Almond (Prunus dulcis)
PATHOGEN: Causal agent unknown
SOURCE: B. Teviotdale