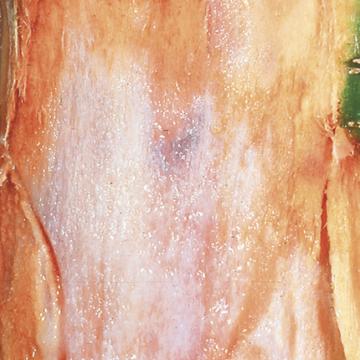DISEASE: Australian citrus dieback
HOST: Citrus (Grapefruit)
Leaves with mottled chlorosis.
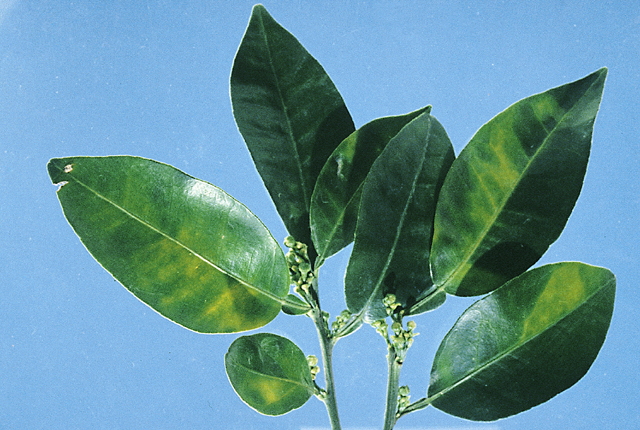

Australian citrus dieback | Citrus (Grapefruit)
DISEASE: Australian citrus dieback
HOST: Citrus (Grapefruit) (Citrus paradisi)
PATHOGEN: 'Candidatus Phytoplasma' sp.
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Phytoplasma (undefined)
SOURCE: P. Broadbent
DISEASE: Australian citrus dieback
HOST: Citrus (Grapefruit)
Late stage of disease. Note yellowing of leaf veins and entire leaves.
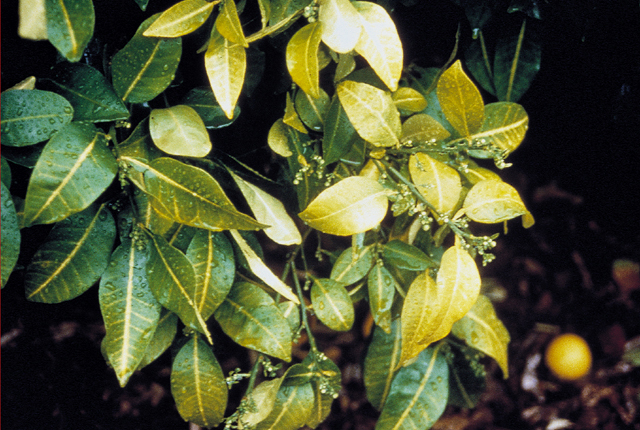

Australian citrus dieback | Citrus (Grapefruit)
DISEASE: Australian citrus dieback
HOST: Citrus (Grapefruit) (Citrus paradisi)
PATHOGEN: 'Candidatus Phytoplasma' sp.
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Phytoplasma (undefined)
SOURCE: P. Broadbent
DISEASE: Australian citrus dieback
HOST: Citrus (Lime)
Severe decline, a late stage of disease. The disease spreads slowly in mature trees, progressing faster in young trees.
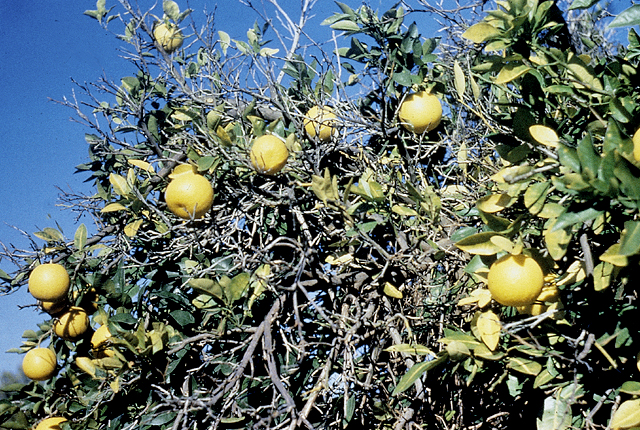

Australian citrus dieback | Citrus (Lime)
DISEASE: Australian citrus dieback
HOST: Citrus (Lime) (Citrus sp.)
PATHOGEN: 'Candidatus Phytoplasma australiense'
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Phytoplasma Stolbur group
SOURCE: P. Broadbent
DISEASE: Bacterial blight (Brown stem)
HOST: Celery
Lesions are necrotic and circular to angular. Some have yellowish halos. Older lesions become brown and dry.

Bacterial blight (Brown stem) | Celery
DISEASE: Bacterial blight (Brown stem)
HOST: Celery (Apium graveolens)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas cichorii
SOURCE: R. Raid
DISEASE: Bacterial blight (Brown stem)
HOST: Celery
Ooze from lesion on celery leaf.
Bacterial blight (Brown stem) | Celery
DISEASE: Bacterial blight (Brown stem)
HOST: Celery (Apium graveolens)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas cichorii
SOURCE: R. Raid
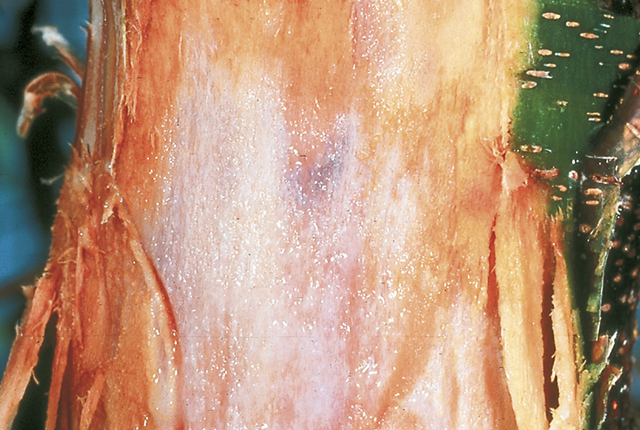
DISEASE: Bacterial blight (Brown stem)
HOST: Celery
Characteristic brown discoloration of petioles, which is more evident on inside of petiole close to the crown. Parenchyma tissues are firm and brown.

Bacterial blight (Brown stem) | Celery
DISEASE: Bacterial blight (Brown stem)
HOST: Celery (Apium graveolens)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas cichorii
SOURCE: K. Pernezny
DISEASE: Foamy canker
HOST: Almond
White, macerated tissues near cambium region is characteristic of disease. Foam is usually associated with cankers. The disease is suspected to be bacterial but the causal agent has not been identified.
Foamy canker | Almond
DISEASE: Foamy canker
HOST: Almond (Prunus dulcis)
PATHOGEN: Causal agent unknown
SOURCE: B. Teviotdale
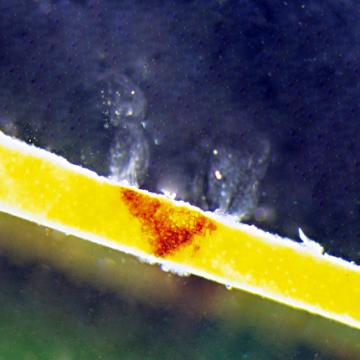
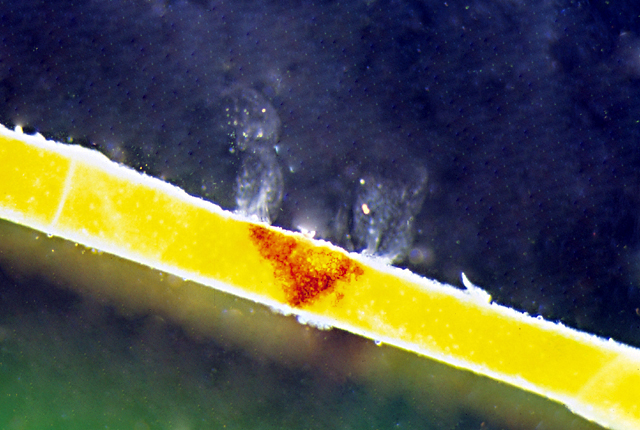
DISEASE: Foamy canker
HOST: Almond
Amber red-colored ooze sliding down the trunk. The causal agent has not been identified.

Foamy canker | Almond
DISEASE: Foamy canker
HOST: Almond (Prunus dulcis)
PATHOGEN: Causal agent unknown
SOURCE: B. Teviotdale