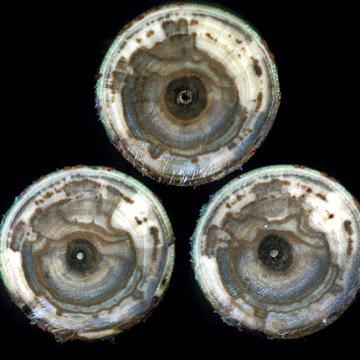
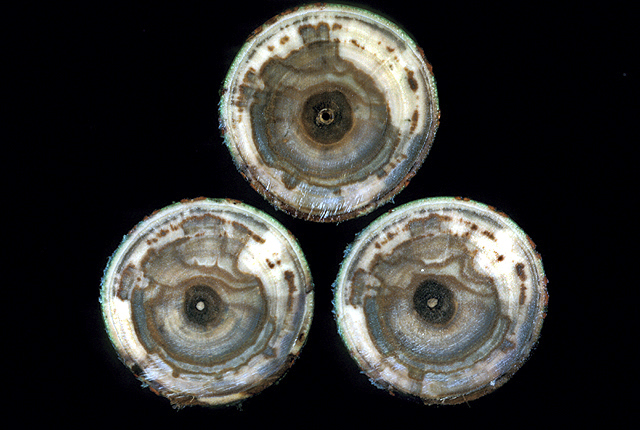
DISEASE: Bacterial wilt and dieback
HOST: Willow
Cross sections of the characteristic "watermark stain" of diseased wood. Wilt and dieback occur as disease progresses.
Bacterial wilt and dieback | Willow
DISEASE: Bacterial wilt and dieback
HOST: Willow (Salix sp.)
PATHOGEN: Brenneria salicis
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Erwinia salicis
SOURCE: Y. Sakamoto, M. Goto
DISEASE: Bacterial wilt and dieback
HOST: Willow
Severely diseased tree with dieback symptoms.
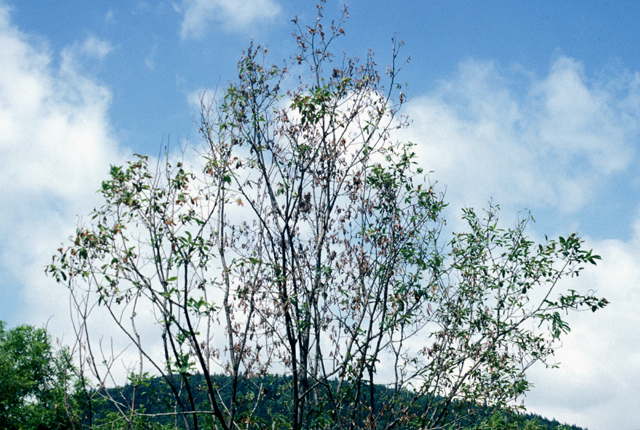

Bacterial wilt and dieback | Willow
DISEASE: Bacterial wilt and dieback
HOST: Willow (Salix sp.)
PATHOGEN: Brenneria salicis
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Erwinia salicis
SOURCE: Y. Sakamoto, M. Goto
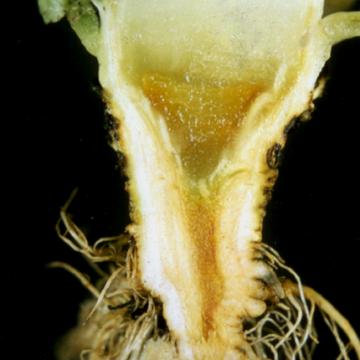
DISEASE: Head rot (Jelly rot)
HOST: Lettuce
Sliced head of lettuce. Typical symptoms are a translucent appearance and browning or jelly rot of the stalk (crown).
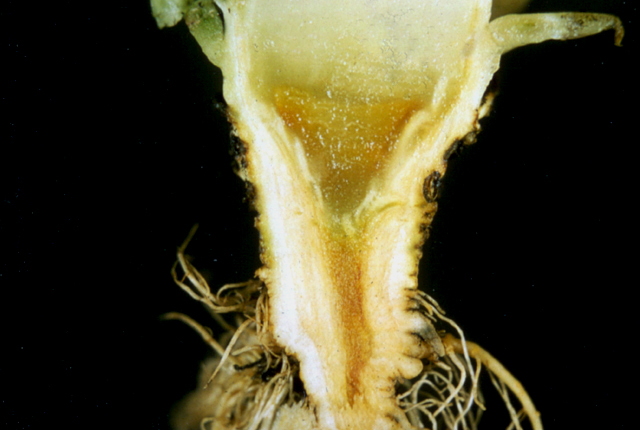
Head rot (Jelly rot) | Lettuce
DISEASE: Head rot (Jelly rot)
HOST: Lettuce (Lactuca sativa)
PATHOGEN: Pectobacterium carotovorum
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora
SOURCE: J. Cho, A. Alvarez
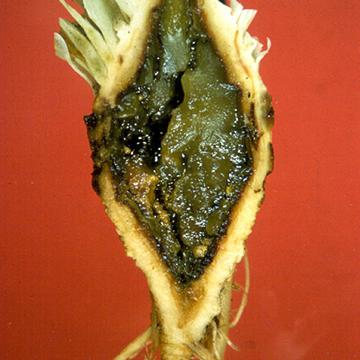
DISEASE: Head rot (Jelly rot)
HOST: Lettuce
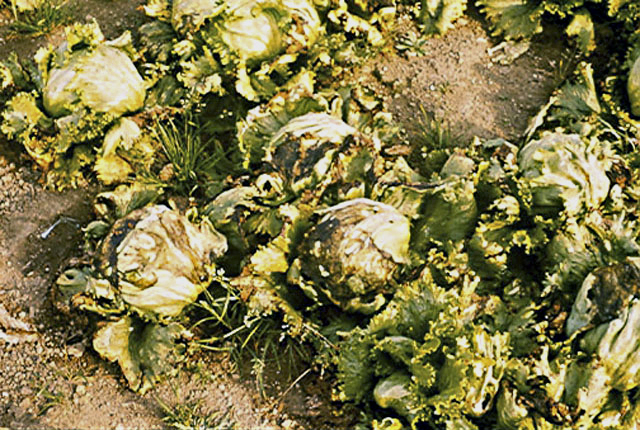
Advanced stage of lettuce stalk rot (crown).
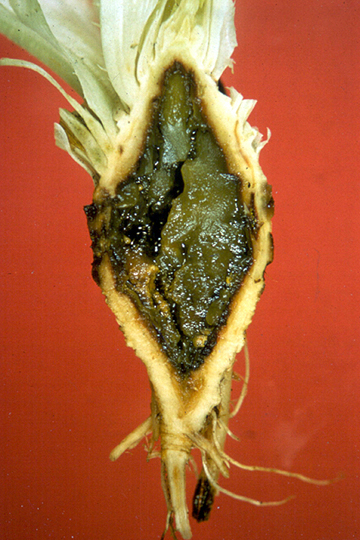
Head rot (Jelly rot) | Lettuce
DISEASE: Head rot (Jelly rot)
HOST: Lettuce (Lactuca sativa)
PATHOGEN: Pectobacterium carotovorum
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora
SOURCE: J. Cho, A. Alvarez
DISEASE: Head rot (Jelly rot)
HOST: Lettuce
Head rot of lettuce first appears as rapid wilt of outer wrapper leaves. Wilt is caused by collapse of vascular tissues, which develop a pinkish to brown discoloration.

Head rot (Jelly rot) | Lettuce
DISEASE: Head rot (Jelly rot)
HOST: Lettuce (Lactuca sativa)
PATHOGEN: Pectobacterium carotovorum
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora
SOURCE: L. Fucikovsky
DISEASE: Syringae leaf spot
HOST: Tomato
Leaves with brown necrotic lesions and chlorotic margins. Symptoms vary greatly among cultivars. Some have black or brown lesions with bright yellow, chlorotic areas and others do not have yellowing.
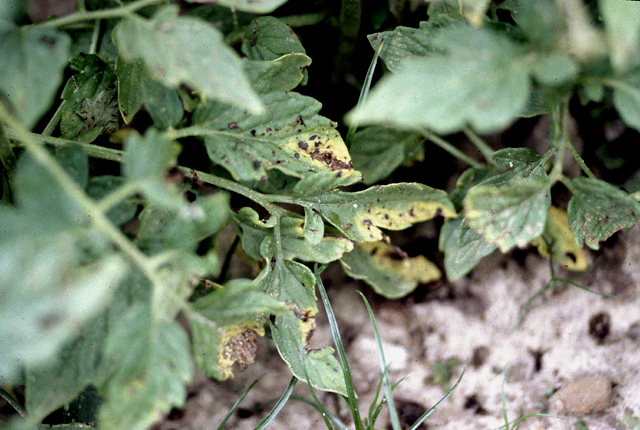

Syringae leaf spot | Tomato
DISEASE: Syringae leaf spot
HOST: Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae
SOURCE: R. Gitaitis