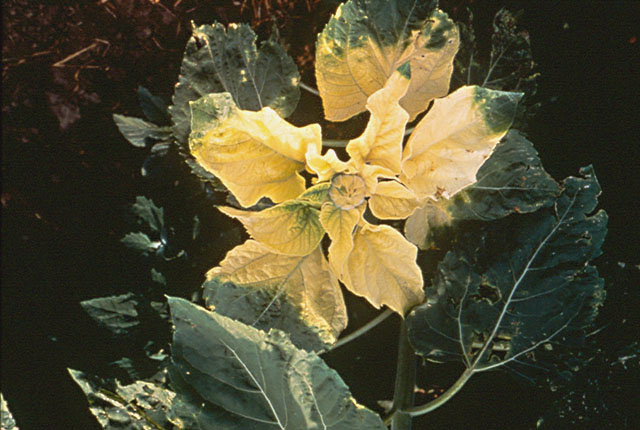
DISEASE: Aster yellows
HOST: Marigold
Infected plant (left) with yellowing and stunting.

Aster yellows | Marigold
DISEASE: Aster yellows
HOST: Marigold (Tagetes erecta)
PATHOGEN: 'Candidatus Phytoplasma asteris'
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Phytoplasma Aster yellows group
SOURCE: M. Shurtleff
DISEASE: Bacterial soft rot
HOST: Orchid
Oncidium orchid with translucence and rot of central leaves.
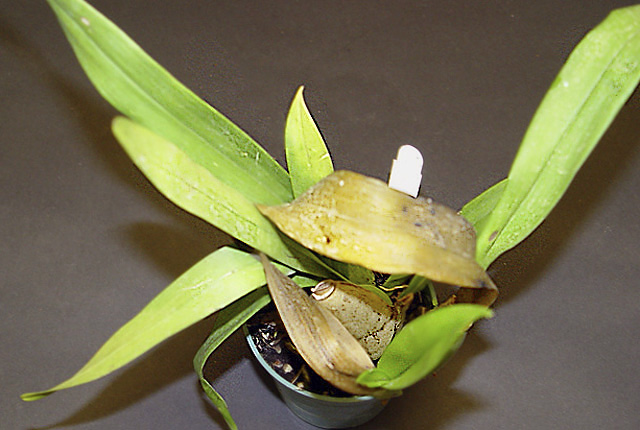

Bacterial soft rot | Orchid
DISEASE: Bacterial soft rot
HOST: Orchid (Oncidium sp.)
PATHOGEN: Pectobacterium carotovorum
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora
SOURCE: R. McMillan
DISEASE: Bacterial stem rot
HOST: Orchid
Oncidium orchid with rot at base of stem.
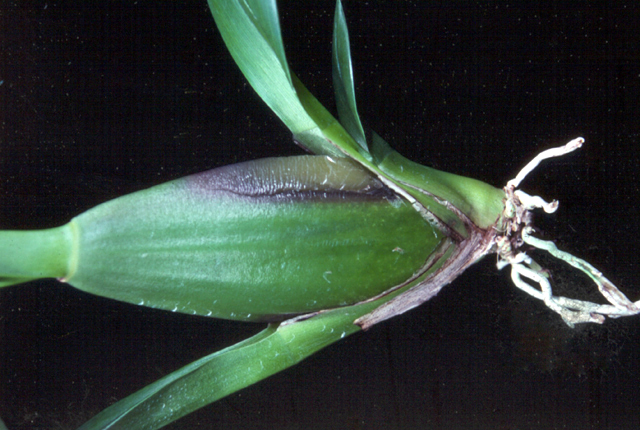

Bacterial stem rot | Orchid
DISEASE: Bacterial stem rot
HOST: Orchid (Oncidium sp.)
PATHOGEN: Burkholderia andropogonis
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Pseudomonas andropogonis
SOURCE: A. Alvarez
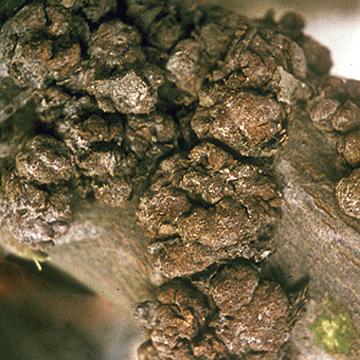
DISEASE: Olive knot
HOST: Olive
Multiple infections of young stems. The bacterium invades vascular tissues during certain times of the year and may be isolated from branches that appear healthy.

Olive knot | Olive
DISEASE: Olive knot
HOST: Olive (Olea europaea)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas savastanoi pv. savastanoi
SOURCE: M. Schroth
DISEASE: Olive knot
HOST: Olive
Tree with knots/galls on branches along with twig dieback, which is associated with knots. Fusarium and Diplodia spp. infect through knots and are thought to be main reason for dieback.

Olive knot | Olive
DISEASE: Olive knot
HOST: Olive (Olea europaea)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas savastanoi pv. savastanoi
SOURCE: M. Schroth
DISEASE: Olive knot
HOST: Olive
Multiple infections on olive branch. Knots at this stage begin to die from the outside in and are infected by several fungi.

Olive knot | Olive
DISEASE: Olive knot
HOST: Olive (Olea europaea)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas savastanoi pv. savastanoi
SOURCE: M. Schroth
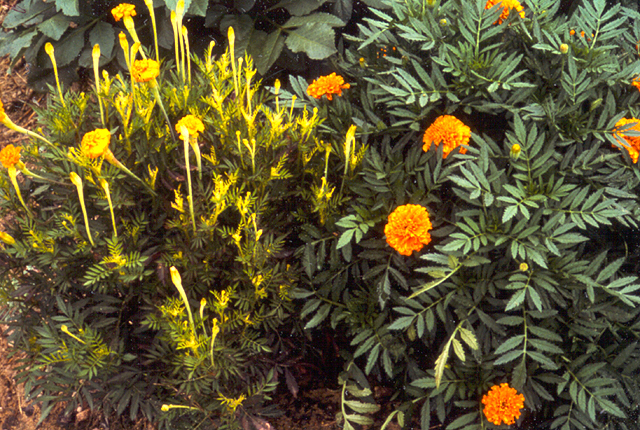
DISEASE: Pseudomonas leaf spot
HOST: Marigold
Marigolds with yellow apical chlorosis attributed to toxin production by the pathogen.
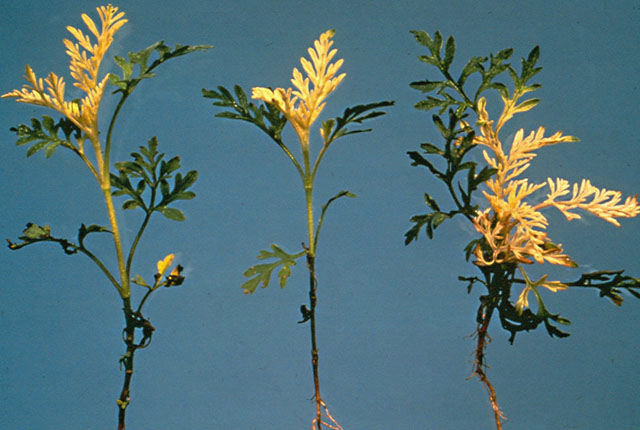

Pseudomonas leaf spot | Marigold
DISEASE: Pseudomonas leaf spot
HOST: Marigold (Tagetes erecta)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas syringae pv. tagetis
SOURCE: R. Durbin