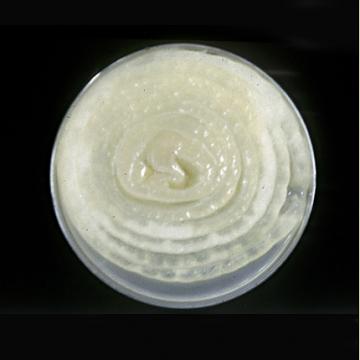
DISEASE: Bacterial flower stalk and leaf necrosis
HOST: Onion
Dark, rotted areas of stalk and leaves caused by systemic invasion of the pathogen.

Bacterial flower stalk and leaf necrosis | Onion
DISEASE: Bacterial flower stalk and leaf necrosis
HOST: Onion (Allium cepa)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas marginalis pv. marginalis
SOURCE: S. Mohan
DISEASE: Bacterial flower stalk and leaf necrosis
HOST: Onion
Gray-brown rot of onion after inoculation. Disease starts as small, water-soaked lesions that later develop into slimy, gray-brown rot. The disease progresses downward from the stalk and may rot the entire bulb.
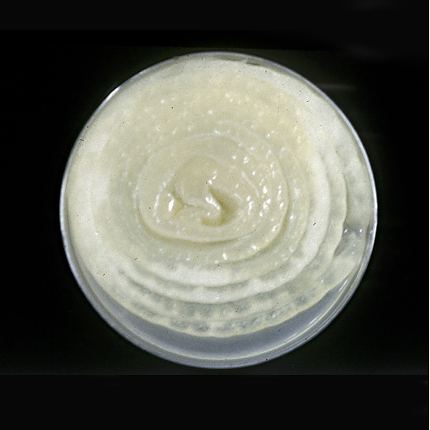
Bacterial flower stalk and leaf necrosis | Onion
DISEASE: Bacterial flower stalk and leaf necrosis
HOST: Onion (Allium cepa)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas marginalis pv. marginalis
SOURCE: R. Gitaitis
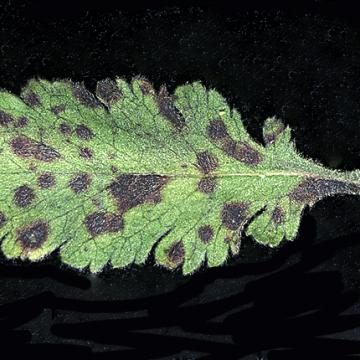
DISEASE: Bacterial flower stalk and leaf necrosis
HOST: Onion
Leaves with necrosis and rot. The common name for this disease is the same as those used for two other diseases. Also, another common name for this disease is bacterial soft rot.

Bacterial flower stalk and leaf necrosis | Onion
DISEASE: Bacterial flower stalk and leaf necrosis
HOST: Onion (Allium cepa)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas marginalis pv. marginalis
SOURCE: S. Mohan
DISEASE: Bacterial foot rot
HOST: Rice
The disease causes sheaths to turn dark brown and rot; dead leaves droop. Nodes, culms, and crowns also decay, and infected tillers are easily detached from the crown. Culms and internodes turn black.

Bacterial foot rot | Rice
DISEASE: Bacterial foot rot
HOST: Rice (Oryza sativa)
PATHOGEN: Dickeya zeae
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Erwinia chrysanthemi pv. zeae
SOURCE: M. Goto
DISEASE: Bacterial foot rot
HOST: Rice
Decayed culms (right) and healthy culms (left). Leaf sheaths of infected plants exhibit dark brown decay and attached leaves turn yellow and wilt.

Bacterial foot rot | Rice
DISEASE: Bacterial foot rot
HOST: Rice (Oryza sativa)
PATHOGEN: Dickeya zeae
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Erwinia chrysanthemi pv. zeae
SOURCE: M. Goto
DISEASE: Bacterial leaf spot
HOST: Laurel (California laurel)
Leaf with dark brown, angular spots.
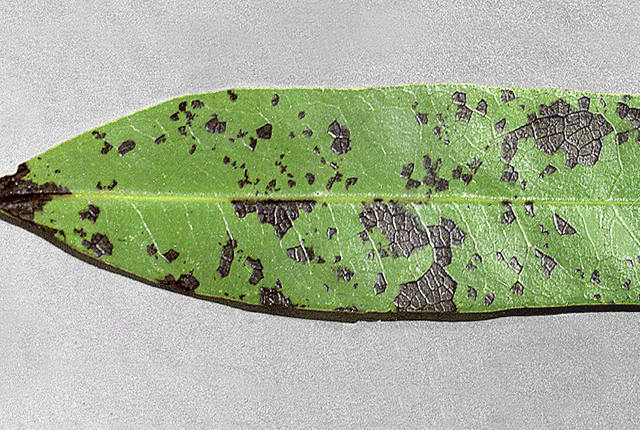

Bacterial leaf spot | Laurel (California laurel)
DISEASE: Bacterial leaf spot
HOST: Laurel (California laurel) (Umbellularia californica)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas sp.
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Pseudomonas lauracearum
SOURCE: W. Sinclair
DISEASE: Bacterial leaf spot
HOST: Peanut
The disease causes water-soaked lesions, particularly on upper leaf surfaces. Lesions enlarge and later display brown necrotic areas. Leaflets become chlorotic and shed prematurely.
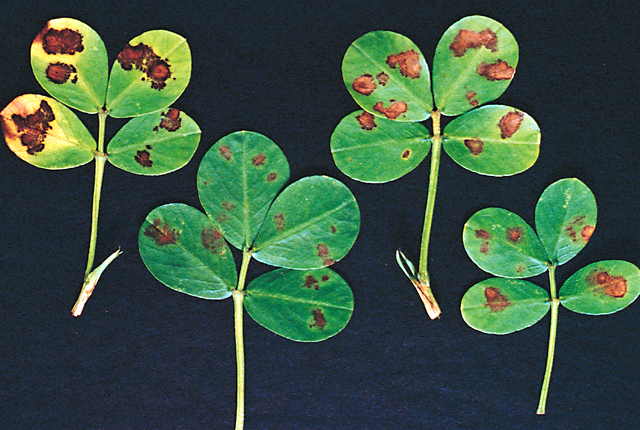
Bacterial leaf spot | Peanut
DISEASE: Bacterial leaf spot
HOST: Peanut (Arachis hypogaea)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas sp.
SOURCE: P. Subrahmanyam
DISEASE: Bacterial leaf spot
HOST: Verbena
Leaf with purple-brown necrotic spots.
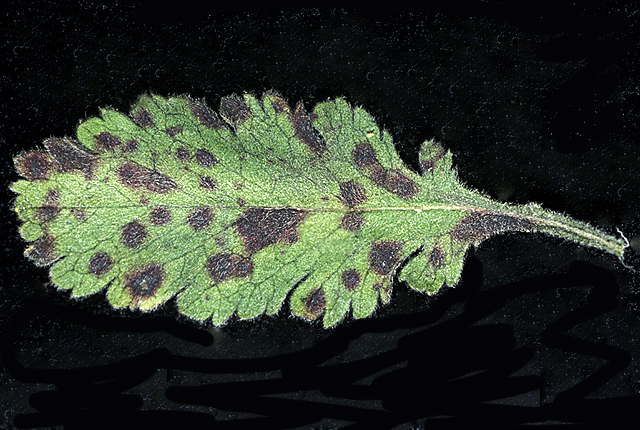

Bacterial leaf spot | Verbena
DISEASE: Bacterial leaf spot
HOST: Verbena (Verbena sp.)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas sp.
SOURCE: R. Raabe
DISEASE: Bacterial soft rot
HOST: Cabbage
Rot of cabbage caused by Pseudomonas marginalis pv. marginalis. Rot caused by P. viridiflava has similar symptoms of water-soaking and blackening of cabbage heads. Both diseases occur mainly during the winter season.

Bacterial soft rot | Cabbage
DISEASE: Bacterial soft rot
HOST: Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas marginalis pv. marginalis
SOURCE: M. Goto