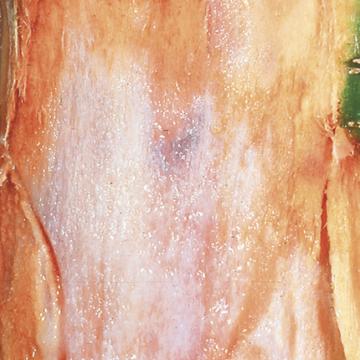DISEASE: Bacterial blight
HOST: Mulberry
Leaf with numerous small, dark brown lesions with chlorotic halos.

Bacterial blight | Mulberry
DISEASE: Bacterial blight
HOST: Mulberry (Morus alba)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas syringae pv. mori
SOURCE: S. Thomson
DISEASE: Bacterial blight
HOST: Mulberry
Foliage with small, dark lesions with large, yellowish halos.

Bacterial blight | Mulberry
DISEASE: Bacterial blight
HOST: Mulberry (Morus sp.)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas syringae pv. mori
SOURCE: M. Sato, M. Goto
DISEASE: Bacterial blight
HOST: Mulberry
Blighted foliage with yellowing and curling of leaves.

Bacterial blight | Mulberry
DISEASE: Bacterial blight
HOST: Mulberry (Morus sp.)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas syringae pv. mori
SOURCE: M. Sato, M. Goto
DISEASE: Bacterial fasciation
HOST: Papaya
Fasciation symptoms of papaya. Causal agent is unknown.

Bacterial fasciation | Papaya
DISEASE: Bacterial fasciation
HOST: Papaya (Carica papaya)
PATHOGEN: Causal agent unknown
SOURCE: A. Alvarez
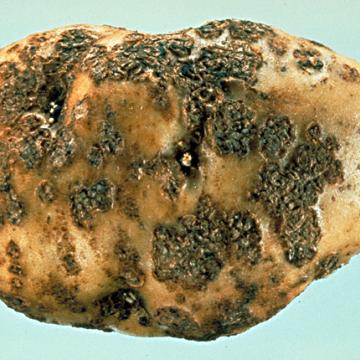
DISEASE: Common scab (Potato scab)
HOST: Potato
Symptoms of common scab vary depending upon the cultivar. The lesions can be shallow or deep, erumpent and corky, and vary in color.
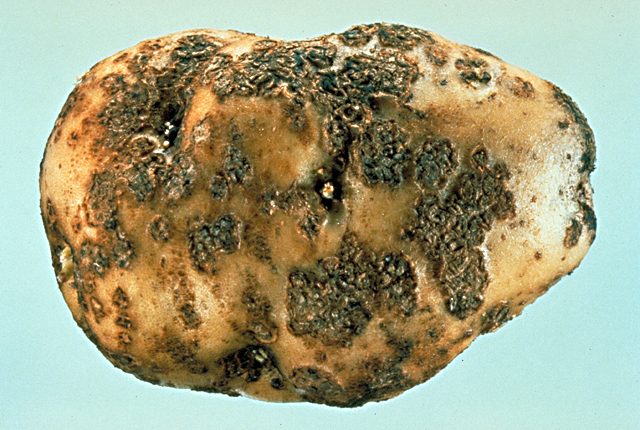
Common scab (Potato scab) | Potato
DISEASE: Common scab (Potato scab)
HOST: Potato (Solanum tuberosum)
PATHOGEN: Streptomyces scabiei
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Streptomyces scabies
SOURCE: A. Secor
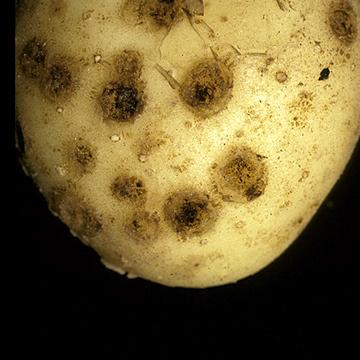
DISEASE: Common scab (Potato scab)
HOST: Potato
White-skinned tuber with sunken and superficial scab lesions.
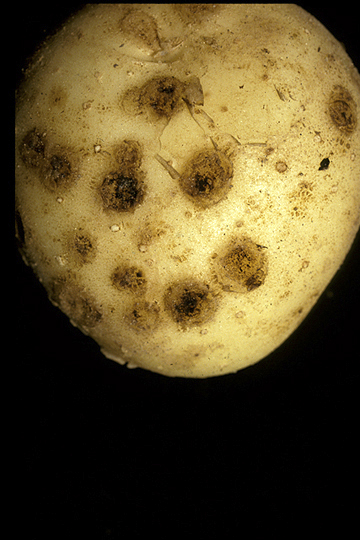
Common scab (Potato scab) | Potato
DISEASE: Common scab (Potato scab)
HOST: Potato (Solanum tuberosum)
PATHOGEN: Streptomyces scabiei
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Streptomyces scabies
SOURCE: S. Thomson
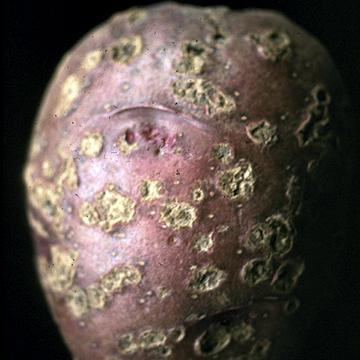
DISEASE: Common scab (Potato scab)
HOST: Potato
Red-skinned tuber with lesions that usually penetrate less than 1 mm.
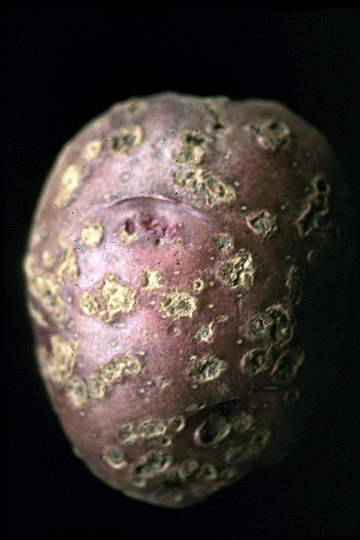
Common scab (Potato scab) | Potato
DISEASE: Common scab (Potato scab)
HOST: Potato (Solanum tuberosum)
PATHOGEN: Streptomyces scabiei
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Streptomyces scabies
SOURCE: S. Thomson
DISEASE: Foamy canker
HOST: Almond
White, macerated tissues near cambium region is characteristic of disease. Foam is usually associated with cankers. The disease is suspected to be bacterial but the causal agent has not been identified.
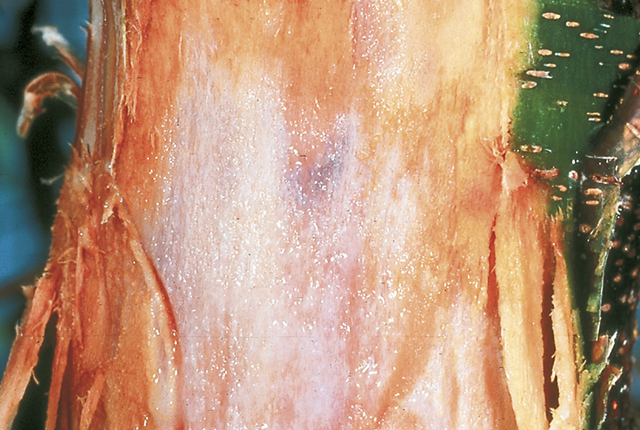
Foamy canker | Almond
DISEASE: Foamy canker
HOST: Almond (Prunus dulcis)
PATHOGEN: Causal agent unknown
SOURCE: B. Teviotdale