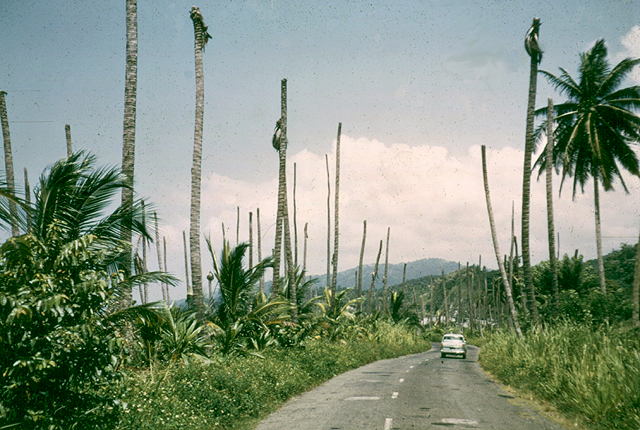
DISEASE: Lethal yellowing
HOST: Palm
Palms near death, noted by yellow fronds, some that have dehisced.

Lethal yellowing | Palm
DISEASE: Lethal yellowing
HOST: Palm (Cocos nucifera)
PATHOGEN: 'Candidatus Phytoplasma palmae'
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Phytoplasma Coconut lethal yellowing group
SOURCE: M. Davis
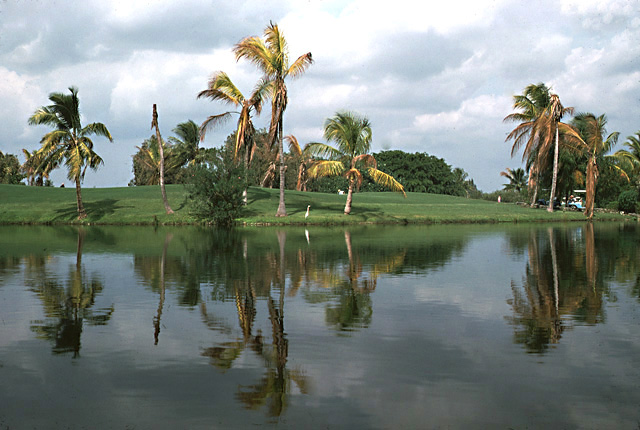
DISEASE: Lethal yellowing
HOST: Palm
Lethal yellowing of palms in Florida. This image was taken shortly after initial outbreak.

Lethal yellowing | Palm
DISEASE: Lethal yellowing
HOST: Palm (Cocos nucifera)
PATHOGEN: 'Candidatus Phytoplasma palmae'
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Phytoplasma Coconut lethal yellowing group
SOURCE: M. Shurtleff
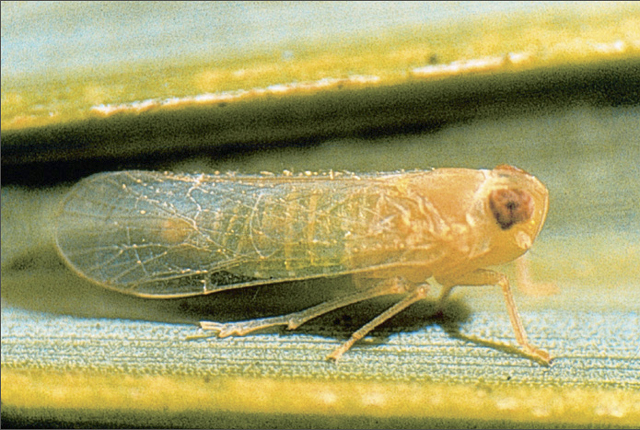
DISEASE: Lethal yellowing
HOST: Palm
Myndus crudus, planthopper, a vector of the lethal yellowing phytoplasma of palms and grasses.

Lethal yellowing | Palm
DISEASE: Lethal yellowing
HOST: Palm (Cocos nucifera)
PATHOGEN: 'Candidatus Phytoplasma palmae'
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Phytoplasma Coconut lethal yellowing group
SOURCE: N. A. Harrison
DISEASE: Lethal yellowing
HOST: Palm
Palm with necrotic inflorescence.
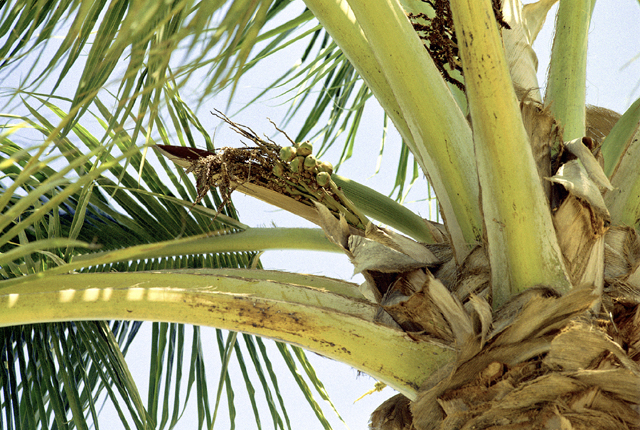

Lethal yellowing | Palm
DISEASE: Lethal yellowing
HOST: Palm (Cocos nucifera)
PATHOGEN: 'Candidatus Phytoplasma palmae'
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Phytoplasma Coconut lethal yellowing group
SOURCE: W. Sinclair
DISEASE: Lethal yellowing
HOST: Palm
Coconut palm exhibiting late stage of disease with chlorotic fronds.
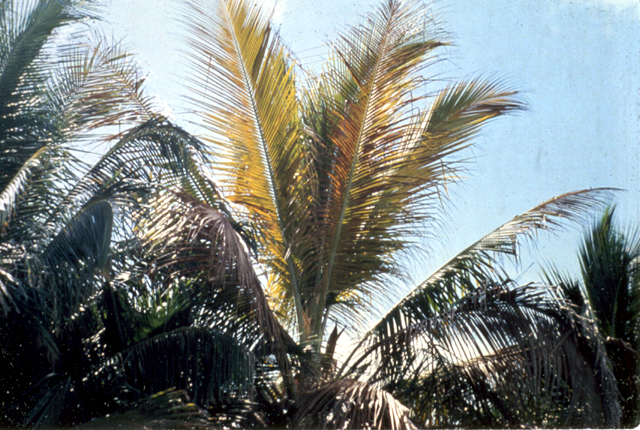

Lethal yellowing | Palm
DISEASE: Lethal yellowing
HOST: Palm (Cocos nucifera)
PATHOGEN: 'Candidatus Phytoplasma palmae'
PATHOGEN SYNONYM: Phytoplasma Coconut lethal yellowing group
SOURCE: A. Martinez
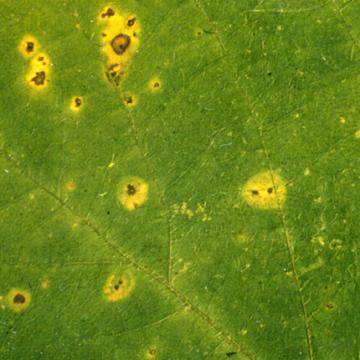
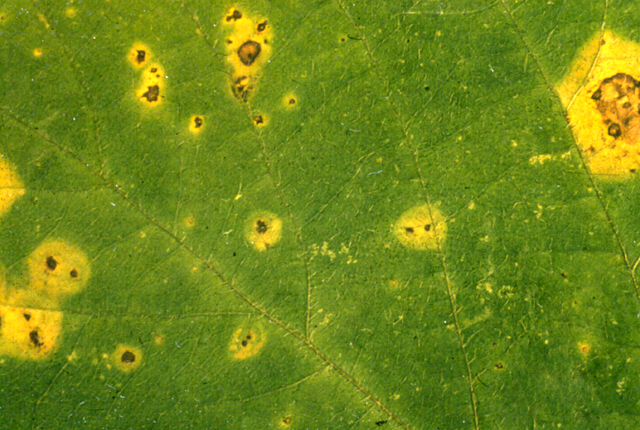
DISEASE: Wildfire (Angular leaf spot)
HOST: Tobacco
Characteristic symptoms are necrotic, brown spots with angular margins surrounded by distinct yellow halos. The halos are caused by the production of tabtoxin.
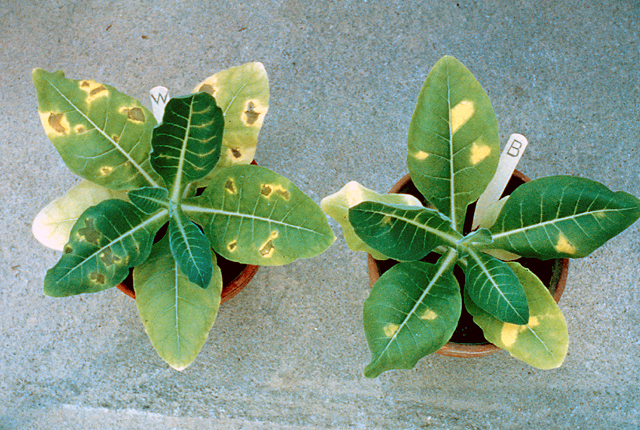

Wildfire (Angular leaf spot) | Tobacco
DISEASE: Wildfire (Angular leaf spot)
HOST: Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci
SOURCE: G. Lucas
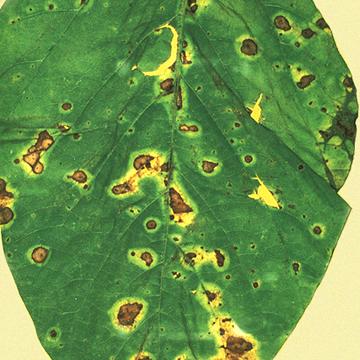
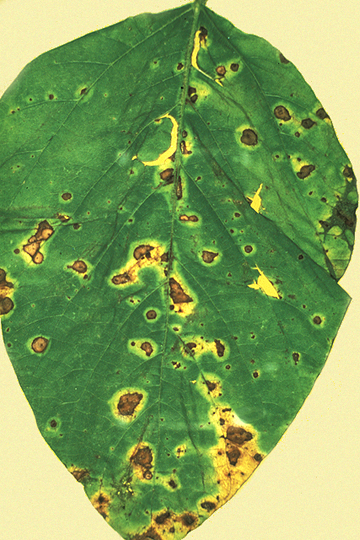
DISEASE: Wildfire
HOST: Soybean
Close-up of lesions with large, yellow halos.
Wildfire | Soybean
DISEASE: Wildfire
HOST: Soybean (Glycine max)
PATHOGEN: Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci
SOURCE: J. Forsberg, M. Shurtleff